

The end of a line marks the end of a statement, so unlike C++ and Java, Python does not require a semicolon at the end of each statement. Like C++ and Java, Python is case sensitive so "a" and "A" are different variables.
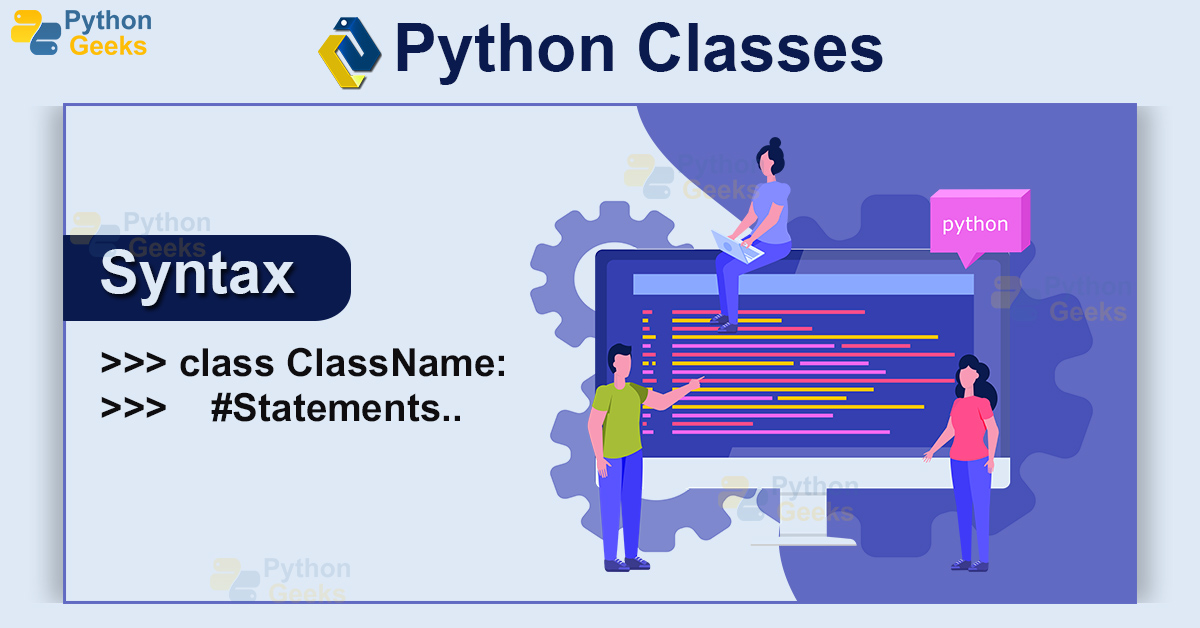
#Python class code#
Also, the interpreter throws, or "raises" in Python parlance, a runtime error if the code tries to read a variable that has not been assigned a value. "Python 3.", these examples should work for you.Īs you can see above, it's easy to experiment with variables and operators. The version of python you're using and where it was built. The two lines python prints after you type python and before the > prompt tells you about > ^D # type CTRL-d to exit (CTRL-z in Windows/DOS terminal) > foo # try something else that doesn't work > a + str(len(a)) # probably what you really wanted TypeError: can only concatenate str (not "int") to str > a + len(a) # try something that doesn't work > len(a) # call the len() function on a string
> a = 'hi' # 'a' can hold a string just as well > a # entering an expression prints its value > a = 6 # set a variable in this interpreter session Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. Python 3.X.X (XXX, XXX XX XXXX, 03:41:42) on XXX If you ever have a question like, "What happens if I add an int to a list?" Just typing it into the Python interpreter is a fast and likely the best way to see what happens. Python tracks the types of all values at runtime and flags code that does not make sense as it runs.Īn excellent way to see how Python code works is to run the Python interpreter and type code right into it. This makes the code short and flexible, and you lose the compile-time type checking of the source code. There are no type declarations of variables, parameters, functions, or methods in source code. Python is a dynamic, interpreted (bytecode-compiled) language. What's this "interpreter" we mention? You'll find out in the next section! Language Introduction Finally, if you're seeking self-paced online learning without watching videos, try the ones listed towards the end of this post - each feature learning content as well as a Python interactive interpreter you can practice with. If you're seeking a companion MOOC course, try the ones from Udacity and Coursera ( intro to programming or intro to Python). As mentioned on the setup page, this material covers Python 3. It is based on the introductory Python course offered internally.

Welcome to Google's Python online tutorial.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
